Everybody falls sick, sometime or the other. For most of us, it becomes call in sick to our place of work & maybe even a hospital admission, costing us a lot of money & a large botheration. But the topic of this discussion here are not about such relative trifles, but the health problems, which are considered to be world’s most dangerous diseases, which have left permanent imprint in our human history. These ailments, some of which are world’s oldest diseases, can truly be considered as one of the greatest natural calamities, that brought humanity to its knees.
Plague has been known to mankind for more than 1500 years. For the uninitiated, Human Plague is a disease caused by a Bacteria, known as Yersinia Pestis, which is found in animals throughout the world. This bacterial infection spreads to humans by fleas (which has previously fed on infected rodents), in areas where there is gross overcrowding of people, living in unhygienic and poor sanitary conditions, with rodent infestation.
There are 3 different types of Plagues are present with some characteristically different manifestations. As this is a disease which can lead to death (it killed millions of people in medieval Europe) if not treated properly, so a brief discussion of different forms of Plague, is warranted here.
Bubonic Plague is the most common variety of Plague, which is acquired from an infected rodent by flea bite. Though less likely, object or material that has come into contact with an infected person, can also be a source of spread of infection. This form of plague, usually affects lymphatic system and causes its inflammation. So, the people may suffer from painful swollen lymph glands, which typically occur in neck, armpits and groins. The swollen lymph nodes are responsible for the characteristic “buboes” that gives this disease its name. Besides this, other common symptoms are – headache, fever with chills, weakness, muscle pain and sometimes seizures.
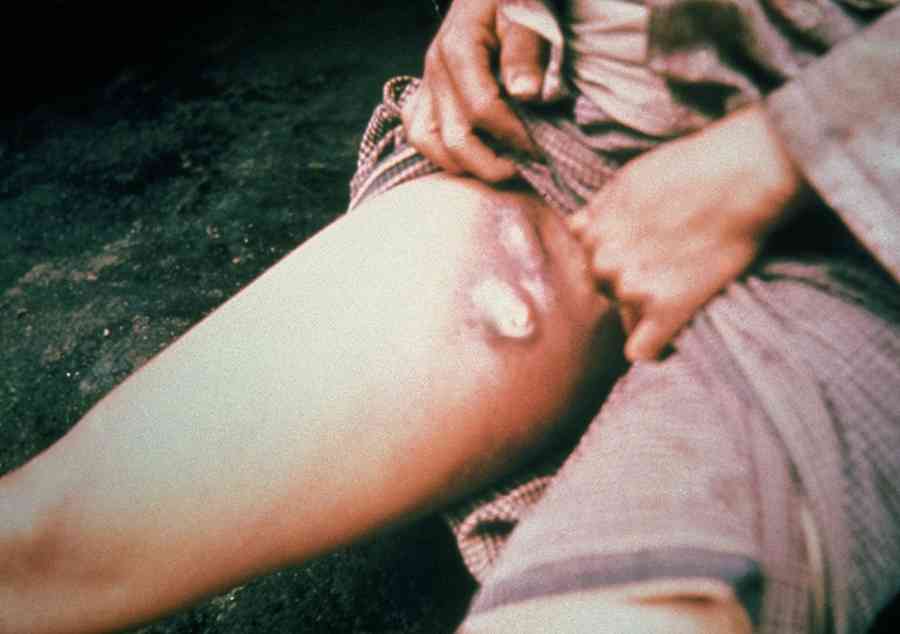
Pneumonic Plague, which is characterised by involvement of the lung. This happens when the bacteria spreads to lungs or more commonly when a patient of pneumonic plague coughs & another person present in close vicinity, breathes in the air containing the infected droplets. The patient presents with difficulty in breathing, cough with bloody sputum and chest pain. Besides, generalised complains like – fever, headache & weakness are also present. This form of Plague, is a lethal form of the disease as it is highly infectious and can lead to an epidemic.
Septicemic plague is caused when the previously mentioned cases of Bubonic Plague and Septicemic Plague are not treated properly, so the bacteria reach blood circulation and starts multiplying. Fever with chills, nausea, vomiting & weakness are present along with abdominal pain, diarrhoea, bleeding, gangrene (Black death) and shock. Needless to say, this can lead to dangerous consequences, if timely care is not taken.
Read More about The Black Death
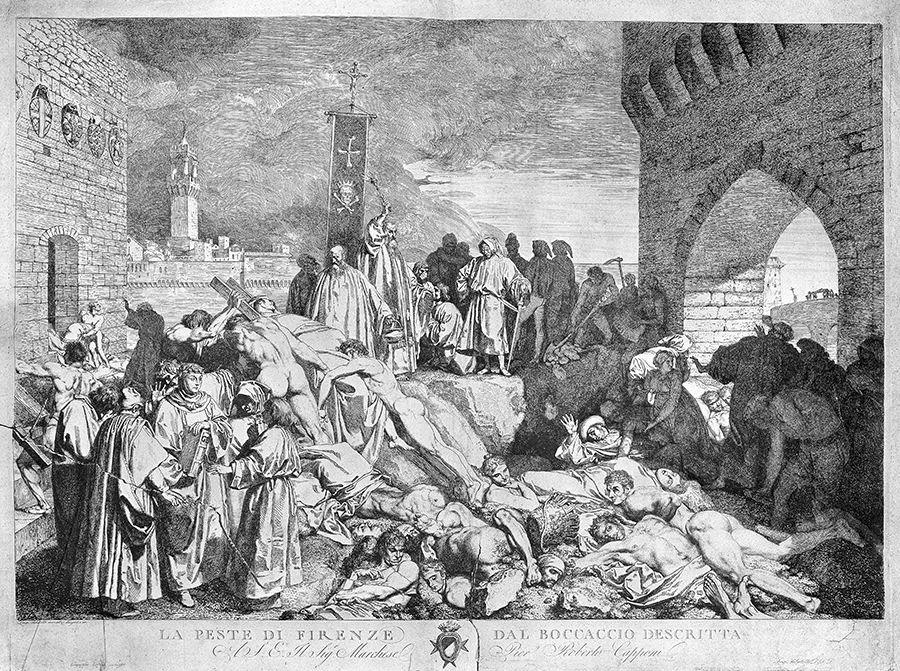
Black Death/ Great Plague/Black Plague is notorious in history as one of the greatest disease epidemics, that spread like wildfire and killed at least 50 million people in Europe and Asia, irrespective of their national identity in 14th century. This epidemic of Plague was caused by the bacteria – Yersinia pestis, which spread by infected rat fleas living off the black rats in merchant ships, plying across the seas in different trade routes. The Black Death was responsible for widespread socioeconomic and religious turbulence in Europe, which occurred in the aftermath of the epidemic.
It is quite obvious by now that Plague as a disease cannot be taken lightly. Timely diagnosis can be made by corelating occupation, travel history, examining details of close contact; with chief complaints. Relevant investigations are undertaken if the diagnosis of Plague is suspected, so as to prevent unnecessary morbidity and mortality.
Smallpox had been around for thousand of years before its global eradication few decades back. But it will never be forgotten. Just 3 centuries back, approximately 400,000 people died each year in Europe from Smallpox. Even those who survived, were not spared from its after effects, as 1/3rd of them became blind and many suffered from extensive scarring of skin.
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by virus. The initial symptoms were just like other viral diseases and characterised by – headache, fever, malaise, muscle pain, nausea & vomiting. Later the skin got involved and characteristic macules appeared in forehead, but soon spread to and involved the entire face, trunks and proximal extremities. Following this, the disease would progress into either of 4 different forms – ordinary, modified, malignant and haemorrhagic; with the last two varieties mostly ending in death. However, in 1796 Edward Jenner discovered a smallpox vaccine. Since then some modifications have been incorporated in the vaccination method, but this intervention has become tremendously successful in controlling smallpox. At present Smallpox has been globally eradicated, with the last natural case reported from Somalia in 1977.
Diphtheria is a bacterial infection, that has been known for more than 2000 years. The cause of Diphtheria is a bacterium – Corynebacterium diphtheriae, which spreads from one person to another usually by contact, but sometimes also by contaminated objects containing the infective agent. As the mucous membrane of the throat and nose are typically involved; so coughing, sneezing or blowing of nose, by an infected person spreads the bacteria in a close area, which can be the cause of infection of people present close by. These people secondarily infected can again spread the infection (for 6 weeks), even if they do not demonstrate obvious signs and symptoms.
Diphtheria symptoms can be rather nonspecific in early stage. Some of these are - sore throat, fever, chill, cough (which sounds like barking) & swollen lymph glands in the neck. However, the most distinct sign is the formation of a thick greyish white coating, in mostly throat area. Some cases also progress to cause more severe features like – difficulty in breathing and/or difficulty in swallowing, slurring of speech, change in vision, and development of signs of shock. Some life-threatening complications can occur due to involvement and damage of heart, nervous system and kidneys; which can manifest as – myocarditis, nerve paralysis and kidney failure respectively.
A vaccination against Diphtheria has reduced the morbidity and mortality considerably. But still in many countries where diphtheria is endemic, a fatality rate of 5-10% is still present, with young children remaining more susceptible to its adverse outcome.
Tuberculosis has been around for many thousands of years, but it is only in late 19th century that important aspects relating to this old disease, started to come into light. This started with discovery of the microbial agent - Mycobacterium tuberculosis (which was proved to be the cause of Tuberculosis) by the German microbiologist Robert Koch in 1892, who subsequently was awarded Nobel Prize in 1905, for his discovery.
Spread of tuberculosis takes place by breathing the air containing infective droplets, coming out from body of a person suffering from active tuberculosis. This can occur via their sneeze, cough or other fluid expulsions. This factor is responsible for the spread of the disease between family members, friends and professional colleagues.
Although most people think that the Tuberculosis just involves the lungs, but that is not necessarily true in every case. Other important organs like – brain and spine may also get involved. This widespread involvement is the reason that it ranks among the main 3 cause of death, in females of age group from 15 to 44 years.
Almost 1/3rd of the world’s population have latent Tuberculosis, in which the causative agent remains latent in the body without spreading the infection or causing any symptoms. However, in smokers and immunocompromised individuals, this condition may change to active tuberculosis, when the individual becomes infective for others and begins to manifest symptoms.
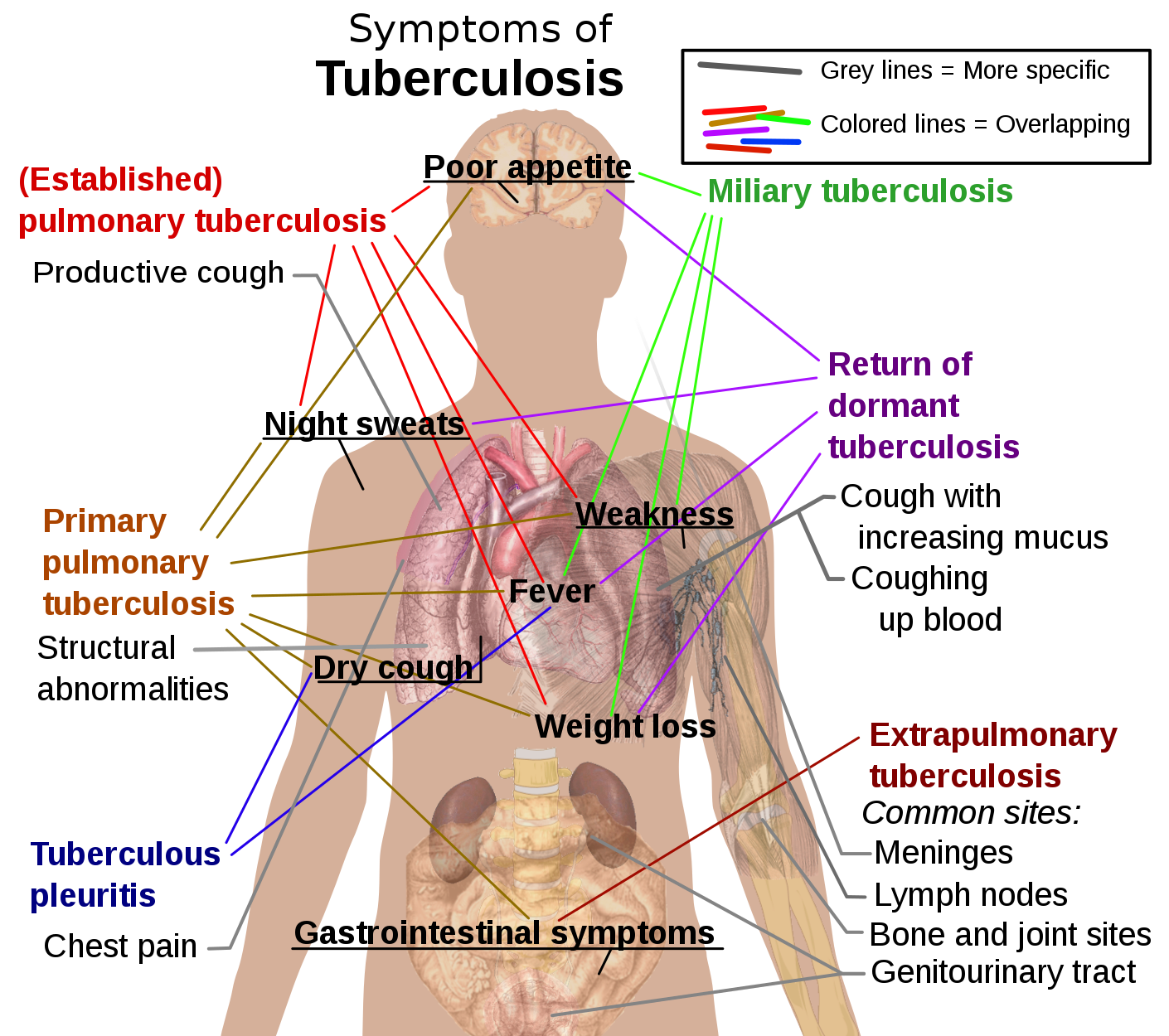
The signs and symptoms of Tuberculosis are – fever with chills and night sweats, loss of appetite and gradual weight loss & cough that stays for a prolong duration (> 3 weeks) and later on is associated with bleeding and pain in the chest. If the tuberculosis affects other parts of the body (which happens if the proper treatment is absent or the patient is immunocompromised), then signs and symptoms, corresponding to the area involved, are produced. In brain, this may cause meningitis; in bones, it will cause pain & structural destruction, involvement of heart, liver and kidney; affects the functioning of these organs. Timely diagnosis and antitubercular treatment in form of antibiotic drug regimen can prevent many unfortunate cases of morbidity and mortality.
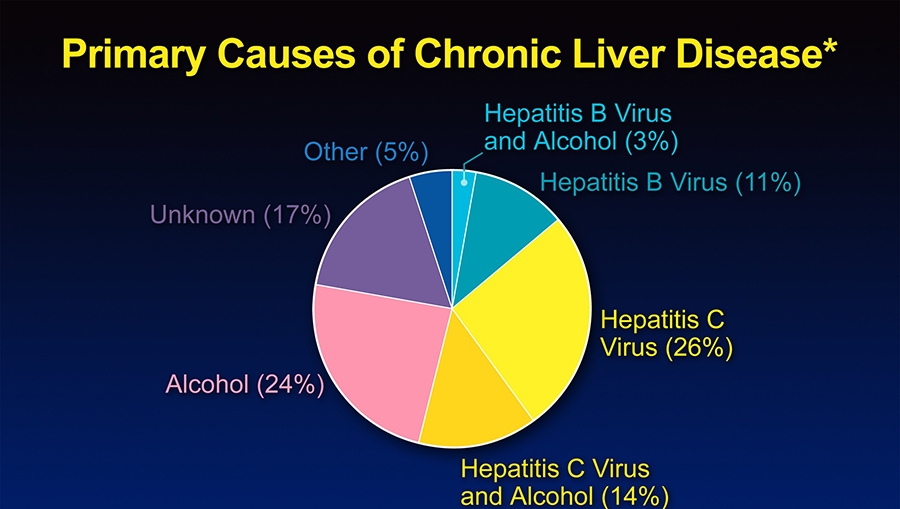
Hepatitis in simple terms means inflammation of liver, that may be caused due to variety of reasons, although viral infection is the commonest cause. Other causes of hepatitis are – medications, alcohol and other toxins. Here it would be prudent to mention that there are 5 different types of Hepatitis, based on viral aetiology.
Hepatitis A is caused by hepatitis A virus; which spreads via food contaminated with faecal matter of an infected individual. Hepatitis B virus is responsible for causing Hepatitis B, which spreads by infected blood or body fluids, as occurs during sexual intercourse. Hence drug addicts sharing needle & people having sexual intercourse with an effected individual; are important reasons for causing and spreading this kind of disease. Hepatitis virus are also responsible for cirrhosis and liver cancers.
Hepatitis C is caused by Hepatitis C virus, the method of spread is the same as Hepatitis B. This is one of the most common viral infections that spreads by blood and is responsible for creating a chronic state of infection & chronic liver disease. It is also one of the main reasons behind Liver cancer and is considered as the most serious type of hepatitis, causing more than 16,000 deaths yearly, in USA alone. Hepatitis D virus is responsible for causing Hepatis D or delta hepatitis. This is a rare form and occurs only in association with Hepatitis B and its mode of spread is by infected blood. Hepatitis E, is caused by Hepatitis E virus and spreads by drinking infected water, containing excreta from an affected individual. This occurs in areas where the sanitation standards are very low.
Hepatitis can present with – nausea, vomiting, fever, weakness, loss of appetite and joint pains. Important signs are – Jaundice causing yellowing of sclera and dark urine. Pale stools and abdominal discomfort also are associated findings. All these signs and symptoms mandates treatment under medical supervision.
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus, which causes HIV infection, and targets the immune system of the human body and thus impairing its function, in such a manner that the human body becomes more susceptible to infections and different cancers. Unfortunately, HIV infection stays lifelong, but with correct treatment, the harmful manifestations can be reduced to a great extent.
As mentioned before HIV is the name of the virus causing the infection, whereas AIDS is the clinical condition. AIDS has emerged as the most feared disease that originated in the 20th century. To understand it better, the Stages of HIV infection has to be understood first. HIV infection spreads by infected blood or by other body fluids like – semen, vaginal secretion, anal fluids; which are transferred by sexual transmission (by unprotected intercourse). Mother to baby transmission can take place during pregnancy, or later through Breast milk. Once a person contacts the virus, the further Stages of HIV infection can be divided into 3 different grades.
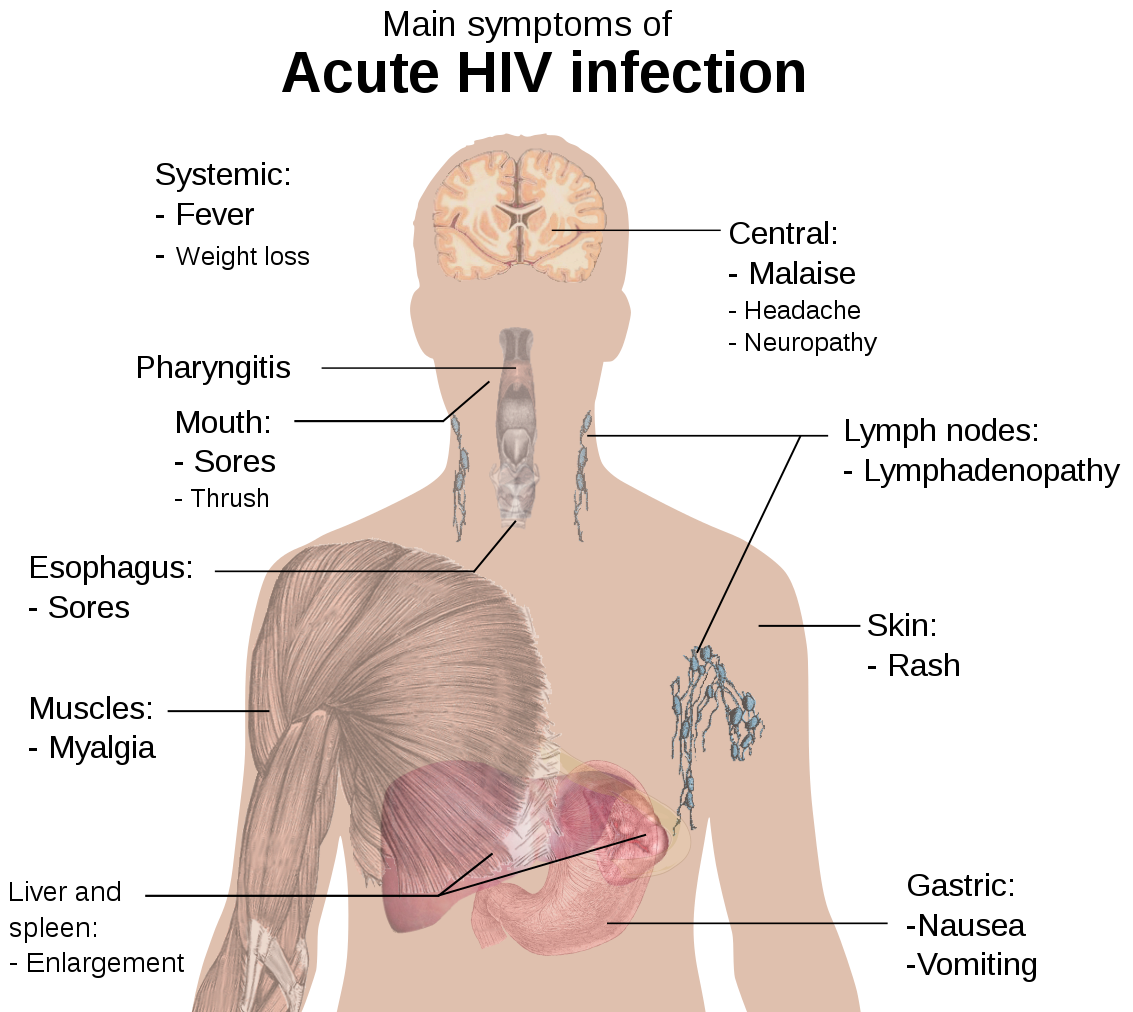
This is the 1st stage of infection, which develops between 2 – 4 weeks of acquiring the infection. During this stage the virus multiplies rapidly and spreads throughout the body and the person affected develops nonspecific symptoms like – headache, fever, rash muscle and joint pain, weakness, night sweats and glandular enlargement. It is during this stage that the virus destroys the protective CD4 lymphocytes of the body, which serves very important role in immune function. The levels of virus in the body is very high in this stage & so is the risk of the virus transmission to another non-suspecting individual.
This is the 2nd stage of HIV infection, that follows the acute stage. This is also called as – asymptomatic HIV infection stage or a clinical latent stage. During this stage the viral multiplication in the body continues, however at a lower level. The people affected may not display any symptoms of the disease, but the transmission of the virus to other people can still take place. Without proper medications and treatment, the disease progresses to the 3rd stage in 10 years (sometimes longer), which is better known as AIDS. However, thanks to modern medical treatments (in form of antiretroviral therapy) progression to stage 3 or AIDS can be prevented in many cases. In other words, this means that many people with HIV don’t always progress to stage 3 disease of AIDS and lead live a near normal life. However, the most important thing to mention here is that, even if AIDS does not develop, the HIV infection never truly goes away.
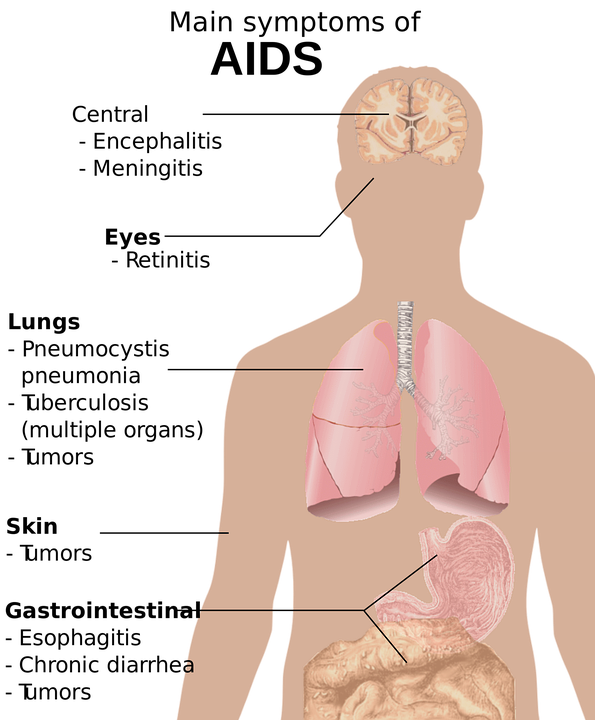
This is the terminal and most severe stage of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection. Diarrhoea, cough, difficulty in breathing, fever, blurred vision, white patches in mouth or tongue and weight loss are commonly seen in this stage. With the immune status of the body being severely impaired, the person becomes susceptible to cancers or even simple infections, which in normal human beings doesn’t have any negative influence on the body. AIDS occurs in a person suffering from HIV infection when the count of CD4 lymphocytes in the body is less than 200 cells/ mm3. Without proper treatment a person suffering from AIDS can survive for at most 3 years, finally succumbing to some opportunistic infections or cancers.
If any person is suspected of having contacted HIV infection by unprotected sexual intercourse, or by use of contaminated needle (in drug abuse) and manifests the signs and symptoms mentioned above in Acute HIV infection, suitable medical opinion should be sought for. After relevant investigations and on confirmation of HIV infection, antiretroviral therapy should be started under medical supervision.
The above-mentioned infectious diseases have wreaked havoc on human society from a very long time. On one hand disease like Smallpox have finally been eradicated by help of modern medicine, but on other hand diseases like HIV infection has emerged as a rather new challenge. However, even HIV infection which couple of decades back was deemed as an entirely hopeless situation, has found new hope in the 21st century. The most important facet of infectious disease is that it can be prevented with the right protections. As the saying goes, prevention is always better than cure & this article is intended as a small step in that direction, by raising awareness among the public regarding the same.
(Disclaimer – The aim of this article is only for raising general awareness among the public and certainly is not a substitute for a direct consultation, with an experienced medical practitioner for those, who are actually suffering from these above-mentioned diseases. Readers discretion is advised.)