Do you love nature and love hiking in areas covered with trees or woods? Does walking among lush green grass thrill your spirit? If so, then a word of caution for you. The innocent view of nature may be quite deceptive and it would certainly help if you first go through the coming lines before you go trekking into the dense grasslands.
Lyme disease is not just the most common tick-borne illness in the continent of Europe and North America but is also the fastest growing vector-borne illness in the United States. Here it would be important to mention that – vector born disease are infections, that are mostly transmitted to humans by the bite of infected insects. According to a report by CDC, Lyme disease has increased by more than an astounding 80% between 2004 to 2016, with an estimate of more than 300,000 cases of Lyme infection in the USA.

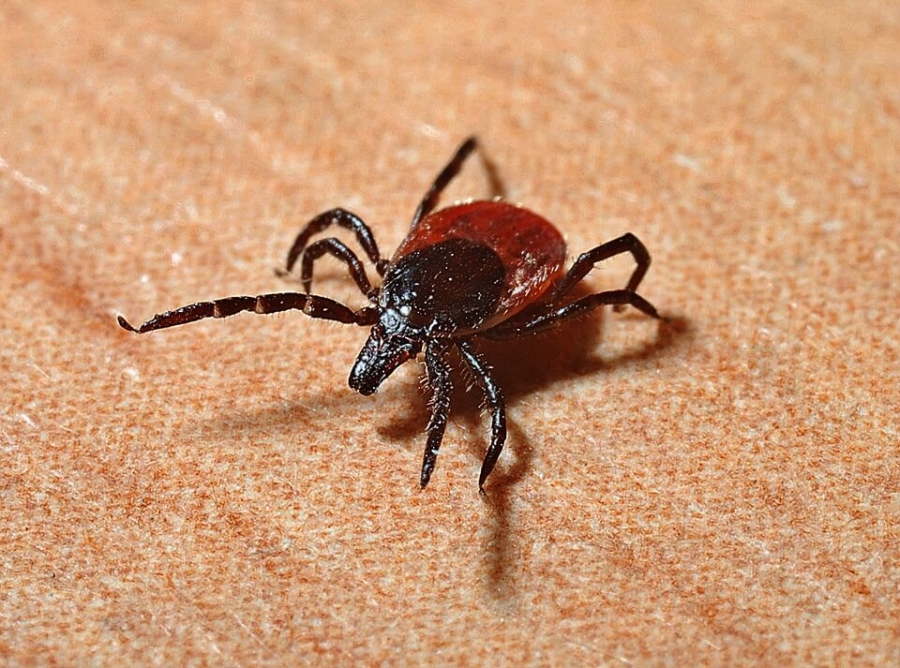
This is a disease caused in humans by the bite of an infected tick (black-legged tick – Ixodes scapularis), during which the bacteria – Borrelia, is transmitted to humans, which is responsible for creating the signs and symptoms of the disease.
Lyme disease is caused by 4 different species of Borrelia, that have been identified as being responsible for mainly causing this disease. In the North American continent, it is Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia mayonii while in Europe and Asia, Borrelia afzelii and Borrelia garinii too can cause the illness. Humans get the infection after tick bite during their excursion into grasslands & bushy areas, inhabited by these tick (containing infected bacteria).
The chances of Lyme Disease developing from Ticks depends on the type of tick that was responsible for the bite, the location of the individual & the duration for which the tick was sticking to the human body. Most black-legged ticks, which are responsible for causing Lyme disease, adhere to the human body for at least 36 to 48 hours. If these ticks are removed within 48 hours, then there are very little chances of getting the infection.
Lyme disease risk factors are concerned with the surrounding environment and lifestyle choices of an individual. As previously mentioned, the deer ticks responsible for causing Lyme disease lives in an area covered with trees or woods, or areas having other lush vegetations. Adults or children, who spend considerable time in this environment are naturally prone to develop Lyme disease.

Venturing out into these areas without covering the skin adequately with proper clothes, increases the probability of skin coming into contact with the infected ticks, which increases the chances of infection. If Housepets wander off into this kind of areas with tall grasses and weeds, they can again promote the spread of infection.
Finally, a person who goes into areas of thick vegetation and does not take precautionary measures to remove ticks attached to his/her body (if he/she is lucky enough to find them), is asking for trouble. Research has shown that a person who removes a tick attached to his body, within 48 hours of its attachment to the human skin, has minimal chances of development of Lyme disease. The crux of the matter – any ticks visibly attached to the skin should be removed as soon as possible.
One of the great difficulties, with diagnosing Lyme disease is the variable time, that takes to develop Lyme disease symptoms. Once the symptoms develop, they can also have multiple different manifestations depending on Lyme disease stages.
These usually develop after 3 to 30 days after a tick bite.
Lyme disease late stages symptoms can develop weeks to months after Tick bite when the primary symptoms are usually not treated in their early stages (because of failure to identify the condition) and they progress. This can manifest as many different symptoms like

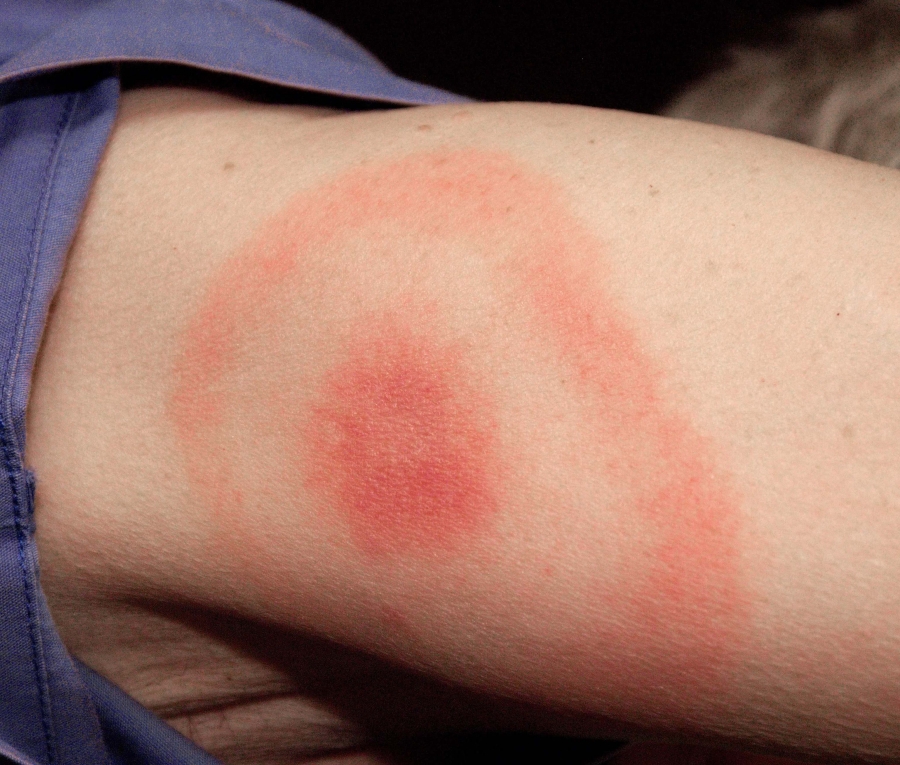
Lyme disease testing is advised by a doctor, when a person has ventured into an area, where deer ticks causing Lyme disease is commonly found (& he/she may have been bitten by a tick) and has developed signs and symptoms mentioned above (with most important being the Lyme disease rash), which raise the suspicion of Lyme disease.
However, many of the signs and symptoms of Lyme disease can be seen in other medical conditions too. Also, in the initial few weeks of the infection, the test reports of the investigation may come back as negative, as antibodies detected in the test take a few weeks to develop (but Lyme disease rash if present, always hints at the disease). The situation is made more complicated by the factor that Ticks, transmit many other diseases besides Lyme disease; but in case of any doubt, it is better to proceed with the investigations – which in this case are blood tests.
The Centre for disease control and prevention, recommends a Two-step Laboratory testing process for Lyme disease, in which blood is tested for antibodies against the bacteria causing Lyme disease. These tests are very reliable a few weeks after the infection. These 2 tests are – Enzyme immunoassay and immunoblot test.
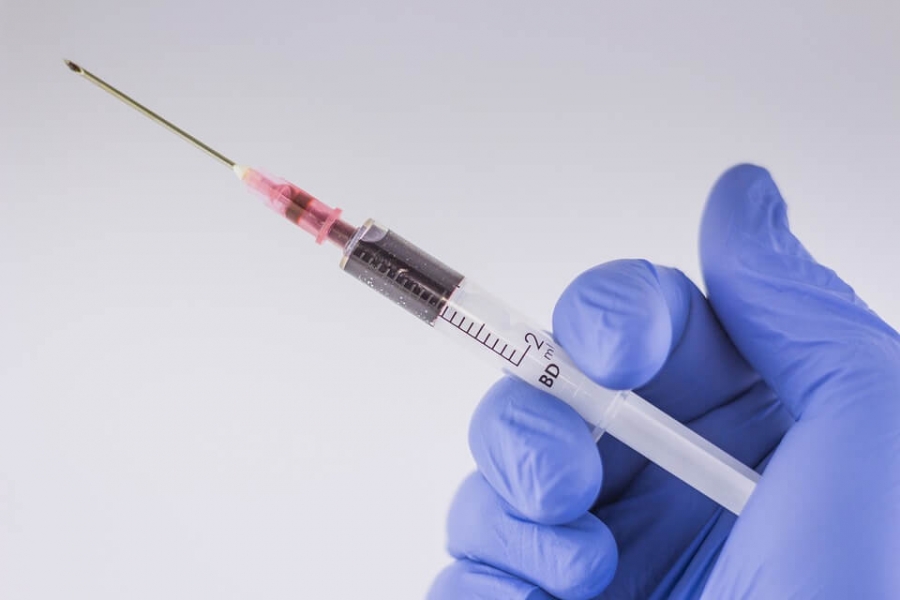
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test is the first test which is done to detect the antibodies to bacteria. If this comes as negative no further testing is required. If the results come as positive a closer look on the case would be required – as this can be false positive results. Sometimes the results may also be indeterminate. In these cases, a second testing step would be required – an immunoblot test. Mostly this is a – Western Blot Test. A person is considered to be suffering from Lyme disease only if both the successive test results come as positive.
Sometimes in more advanced cases having involvement of the central nervous system, as evident by signs and symptoms of meningitis, testing the cerebrospinal fluid collected by lumbar puncture may be required.
Lyme disease in humans is an infection, which can cause serious problems if left untreated. Hence it is imperative that the condition is diagnosed as soon as possible and treatment is started as fast as possible for rapid improvement.
Antibiotics are used to treat Lyme disease, the most common being – doxycycline, amoxicillin or cefuroxime. Doctors usually prescribe an antibiotic course for 14 to 21 days, but sometimes a course of 10 to 14 days may also suffice.
In some instances, if the disease is advanced in some cardiac or neurological form of illness, then intravenous use of antibiotics like – penicillin or ceftriaxone may be needed. As these medications can cause some side effects, it should be taken only under the supervision of a doctor.

The vast majority of people treated with the proper antibiotics in early stages recover quickly and completely. However, Post Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome/Post Lyme Disease syndrome describes a situation (occurring only in a small fraction of patients) in which a patient who has already completed his treatment, still complains of non-specific symptoms like – muscle and joint pain & tiredness. The cause of post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome/ post Lyme disease syndrome is not known and further treatment with antibiotics is not useful.
As has been discussed earlier, the best way to protect yourself from this disease is by avoiding exposure to the disease-causing deer ticks, which live on grassy, brushy, or wooded areas. If for some reason a person is forced to visit the areas known to harbor the ticks responsible for Lyme disease, then they should take adequate protection.

Everyone who habitually, likes walking among tall grass or in the woods or has gardening as a hobby or a job, should afterward check their skin once they are done. The ticks responsible for Lyme disease are very small and that of a size of a poppy seed so can be easily missed if they are not searched for with great care. The best way to do this would be in a shower while taking a bath. If the ticks are removed from the skin, within 36 to 48 hours of exposure then chances of infection are minimal.
Even those who have been infected & suffered from Lyme disease previously should know and remember the fact that even if a person has suffered from Lyme disease before, he/she is not immune from further attacks. Lyme disease can occur more than once. If Lyme disease rash is present, after an excursion to exposure prone area, then it is a sign that tick bite is present and antibiotic treatment under medical supervision would be needed. Even if the Lyme disease rash is not present, but nonspecific flu-like symptoms are present then, a medical opinion should be asked for.
It is estimated by the year 2050, 12% of the population of the USA and 17% of the population of Europe will be infected by Lyme disease. The health problem imposes quite a significant economic burden to even the developed countries like – USA. Awareness regarding the disease and timely proper management can do a lot to decrease the suffering of the affected individuals, which is the aim of this article.
(Disclaimer – This article is written with the sole purpose of raising awareness among the general population. It is not a substitute for direct medical consultation with a health professional. Reader’s discretion is advised.)